
A peaceful and fully typed MyAnimeList / Jikan Python API wrapper with caching and proper rate limiting.

Note
Anmoku is currently a work in progress so the features below may not be complete yet or experimental.
- Rate limiting 🎀 (with actual waiting).
- Supports caching. ⚡
- Fully type hinted. 🌌
yes you heard me correctly
Anmoku is probably the simplest Jikan API wrapper you’ll ever use. All you need is the client and the resource. 🌊
from anmoku import Anmoku, AnimeCharacters
client = Anmoku(debug = True)
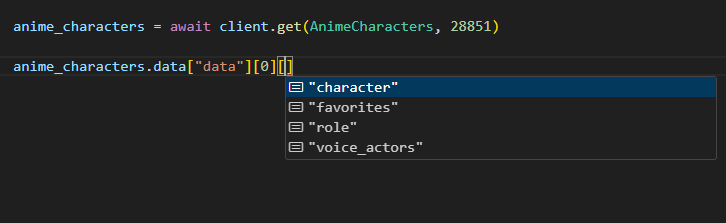
anime_characters = client.get(AnimeCharacters, id = 28851) # ID for the anime film "A Silent Voice".
for character in anime_characters:
print(f"{character.name} ({character.url})")
client.close()We also have an async client:
import asyncio
from anmoku import AsyncAnmoku, AnimeCharacters
async def main():
client = AsyncAnmoku(debug = True)
anime_characters = await client.get(AnimeCharacters, id = 28851) # ID for the anime film "A Silent Voice".
for character in anime_characters:
print(f"{character.name} ({character.url})")
await client.close()
asyncio.run(main())[DEBUG] (anmoku) - [AsyncAnmoku] GET --> https://api.jikan.moe/v4/anime/28851/characters
Ishida, Shouya (https://myanimelist.net/character/80491/Shouya_Ishida)
Nishimiya, Shouko (https://myanimelist.net/character/80243/Shouko_Nishimiya)
Headteacher (https://myanimelist.net/character/214351/Headteacher)
Hirose, Keisuke (https://myanimelist.net/character/97569/Keisuke_Hirose)
Ishida, Maria (https://myanimelist.net/character/97943/Maria_Ishida)
Ishida, Sister (https://myanimelist.net/character/118723/Sister_Ishida)
# ... more characters below but I cut them off for the convenience of this readmeHere are some searching examples you can try:
from anmoku import Anmoku, Character
client = Anmoku(debug = True)
characters = client.search(Character, "anya forger")
for character in characters:
print(f"{character.name} ({character.image.url})")
client.close()Merge that with gradio and you have a GUI.
anmoku/examples/gradio_anime_search.py
Lines 1 to 23 in 099f659
gradio_gui.mp4
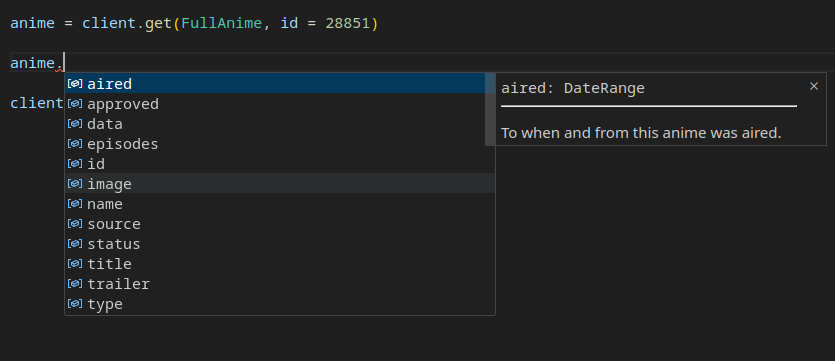
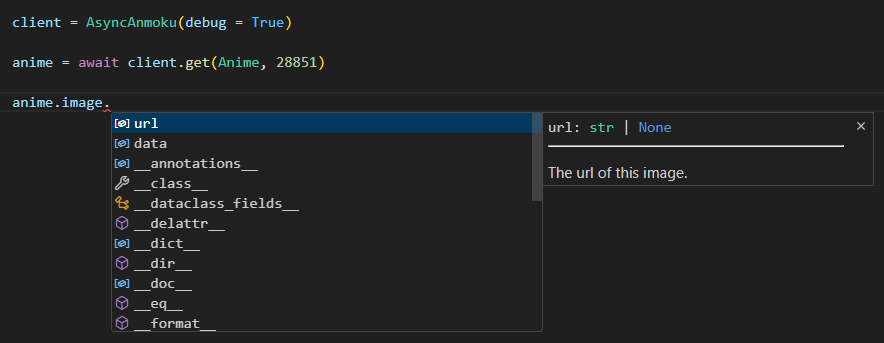
API responses in our library are strongly typed.
On top of that, we even provide class interfaces if you wish for stability and ease of use.
 https://github.com/THEGOLDENPRO/anmoku
https://github.com/THEGOLDENPRO/anmoku